Whey protein is one of the highest quality protein sources available. However, not all whey proteins are the same in composition; they differ in their production processes, which affects their composition nutritional value. How is whey protein produced, and how to choose a product that contains the highest proportion of beneficial substances for the body?
Step by step: How is whey protein produced?
1. Separation of Whey from Milk
Whey protein is made from cow's milk. Whey protein makes up about 20% of milk protein, meaning more than 100 litres of cow's milk are needed to produce 1kg of the resulting protein.
The first step involves separating the whey, by adding chymosin as a rennet to the milk. This action precipitates the casein (the remaining component of milk protein) and diverts the whey for further processing. The precipitated casein is further used to make cheese or curd.
However, the whey processed in this way still has a long way to go before it becomes whey protein. On average, it has approximately the following composition:
| Nutrient content (g/100 g) | |
| Protein | 13 |
| Carbohydrates (lactose) | 83 |
| Fats | 1 |
Dried sweet whey in this form is popularly used in infant formulas or carbohydrate drinks (gainers). However, it needs to be further processed to produce whey protein.
2. Concentrating the Whey Protein
Although sweet whey has nutritional value, it doesn't compare to that of whey protein. Now is the time to concentrate the proteins present in the whey, thereby increasing their percentage in the dry matter.
Traditionally, ultrafiltration has been the method used for this initial stage. In this process, proteins are retained on semi‑permeable membranes while smaller molecules (such as milk sugar - lactose) pass through the membrane. However, there is a significant drawback with ultrafiltration at this stage - residual milk fat is also retained on the semi‑permeable membrane. As a result, an 80% whey protein concentrate might still contain 7‑8 % residual fat.
It is then possible to concentrate the protein by ion exchange to form whey isolate. This method, however, disturbs the native protein structure and alters the ratios of the basic peptide types in the whey protein.
A more refined solution emerged in the 1990s with the advent of CFM (cross‑flow microfiltration). In CFM, filtration occurs perpendicular to the direction of whey passage. In this way, it is possible to obtain a whey concentrate containing 80% protein with only a minimal amount of fat. Subsequent ultrafiltration of the concentrate thus prepared can lead to a whey protein isolate containing approximately 90% protein. The CFM method can be seen in more detail in the following figure.
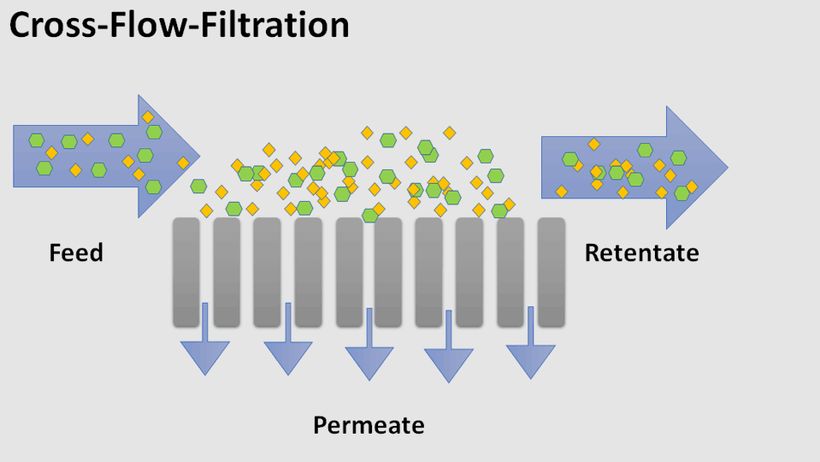
"Feed" represents the whey entering the filters and the direction of flow,."Permeate" represents the whey concentrate obtained. "Retentate" refers to substances that have been retained by the membrane.
3. Drying the Filtered Whey Concentrate
CFM filtration produces a concentrate largely free of residual carbohydrates and fats. However, it still contains a high proportion of water, which needs to be removed. Inappropriate or overly gentle drying approach could lead to the denaturation of native peptide fractions. For this reason, spray drying is used, a method in which small droplets of the original raw material are dried quickly and gently to remove water.
Whey protein is a world away. In concentrates, the protein content is about 80%, while isolates can contain more than 90%. Above all, residual sugars (lactose) and fats are still present in the concentrate, but these are minimal in a single dose of protein drink. Beyond the basic macronutrients, whey proteins are relatively rich in calcium, although they contain slightly less magnesium or iron.
How are whey proteins flavoured?
Unflavoured whey protein itself has a rather pleasant milky taste, so adding flavour usually does not cause any major complications for manufacturers. In most cases, the popular triple flavouring combination of flavouring, colouring and sweetener is used. If the flavouring is natural (e.g., stevia), you will find a mention of this in the ingredients, and the same goes for the colouring. In the majority of cases, artificial sweeteners (sucralose) with a high sweetening power are used as sweeteners, as it is not entirely desirable to supplement a whey protein concentrate that has just been stripped of milk sugar (lactose) with conventional sugar.
Whey protein is already available in this form from food supplement manufacturers. Guar gum and soya lecithin, which improve the structure and texture of protein drinks, may also be added to further supplement them.
Our Vilgain Grass‑Fed Whey Protein is a low‑temperature ultra‑filtered whey protein concentrate (WPC) that is naturally sweetened with stevia only and flavoured with natural ingredients.
Grass‑Fed Whey Protein

Bottom line
The production of whey protein involves several consecutive steps. First, sweet whey is extracted from the milk and from this, the whey protein is then concentrated.In the final step, the captured protein is dried into a powder, as we know it from dietary supplement manufacturers. It is certainly not a product that undergoes many chemical reactions. In most cases, the pure unflavoured product is just processed whey from milk, which is purely natural in origin.
When choosing whey protein, we should also look at the production method. For us, the CFM label means the assurance of gentle processing that preserves the native structures of the peptides present, which is a nice plus. In addition, the ratio between the different types of peptides is preserved in this way, which is another advantage over whey isolates produced by ion exchange, which, among other things, removes rapidly absorbed glycomacropeptides.
In terms of flavouring, prefer products that have a simple and clear composition. Natural colouring, natural flavouring and stevia as a sweetener is a pleasant triple combination that is abundantly sufficient to flavour whey protein. On the other hand, filler sugars such as maltodextrin or dextrose are not desirable in larger quantities.

















